1. Introduction to CBRS: Understanding the Citizens Broadband Radio Service
- What is CBRS? The Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) is a wireless spectrum band regulated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the 3.5 GHz range. Originally allocated for government use, this band was opened up by the FCC to meet growing demand in public and commercial wireless networks.
- Core Features of CBRS:
- Spectrum Sharing: CBRS operates as a dynamic spectrum-sharing model, allowing multiple types of users to access the same band without exclusive rights.
- Three-Tiered Priority Structure: CBRS uses a three-tiered user priority structure to manage spectrum allocation, divided into Incumbent Access, Priority Access Licenses (PAL), and General Authorized Access (GAA).
2. Role of Google SAS: Managing and Optimizing Spectrum Access
- What is Google SAS? The Google Spectrum Access System (SAS) is a sophisticated spectrum management platform developed to dynamically allocate and manage access to the CBRS band. This system prevents interference between users, providing fair access and optimal performance.
- Goals of Google SAS:
- Facilitate Spectrum Sharing: Using intelligent algorithms and dynamic spectrum allocation, SAS efficiently shares spectrum across different user types.
- Enhance Bandwidth and Transmission Power: SAS enables users to maximize bandwidth and maintain optimal transmission power, delivering reliable connectivity for a range of network needs.
3. Three-Tiered Priority Structure in CBRS SAS
- Incumbent Users (Tier 1): Government and military users occupy the top tier, having full control over the spectrum whenever needed.
- Priority Access License (PAL) Users (Tier 2): PAL users, including commercial businesses, gain priority through auctioned licenses, securing more consistent access than GAA users.
- General Authorized Access (GAA) Users (Tier 3): These users access spectrum opportunistically without paying for licenses and must defer to Incumbent and PAL users when required.
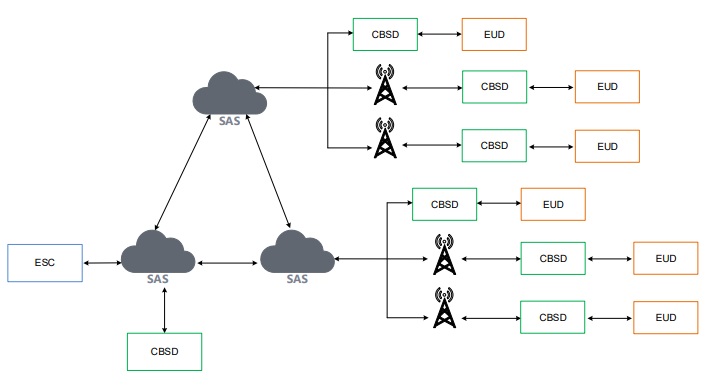
4. Key Components of the Google SAS Architecture
- Environmental Sensing Capability (ESC): A monitoring system that detects Incumbent user activity to ensure lower-priority users cease transmission when higher-priority users need access.
- Database Management System: Stores and tracks essential data on all CBRS devices, including location, user priority, and operational status.
- Device Registration Module: Any CBRS device must register through Google SAS to receive permission for spectrum access.
- Spectrum Allocation Algorithms: Advanced algorithms manage spectrum distribution among users, ensuring optimal efficiency and minimizing interference.
5. How Google SAS Operates: Enabling Spectrum Sharing
- Device Registration and Authentication: Each CBRS device must register with Google SAS, providing location, transmission power, and usage type information for management.
- Spectrum Requests and Allocation: Once a device requests access, SAS analyzes spectrum availability, assigning a suitable band to maintain optimal efficiency.
- Dynamic Spectrum Adjustment: When Incumbent users or higher-priority users need the spectrum, SAS notifies lower-tier users to either pause usage or shift to a different band, ensuring that priority access is maintained seamlessly.
6. Security and Privacy in Google SAS
- Data Encryption: All data transmitted within SAS is encrypted to protect information from unauthorized access.
- Device Authentication: SAS enforces strict authentication for devices, preventing unauthorized access to the spectrum.
- Privacy Safeguards: Google SAS applies stringent privacy protocols when handling and sharing user data, ensuring security and confidentiality.
7. Benefits of Google SAS: Shaping the Future of Wireless Networks
- Efficient Spectrum Utilization: By allocating spectrum dynamically, SAS maximizes the use of available frequencies.
- Support for Private and Enterprise Networks: SAS facilitates easy spectrum access not only for traditional telecom operators but also for private and enterprise networks, supporting the expansion of 5G and IoT.
- Automated Spectrum Management: SAS automation reduces the need for manual intervention, improving resource allocation and maximizing usage efficiency.
8. Application Scenarios of CBRS SAS: Beyond Traditional Mobile Networks
- Fixed Wireless Access (FWA): CBRS provides a high-speed broadband solution, especially beneficial for underserved rural and remote areas.
- Enterprise and Industrial Networks: CBRS offers a reliable spectrum option for enterprises, enabling them to establish high-performance private networks in office buildings, campuses, and industrial sites.
- Mobile Network Expansion: CBRS is a significant spectrum resource for 5G, reducing dependence on exclusively licensed bands and facilitating carrier expansion.
9. The Future of CBRS SAS: Advancing Wireless Communication
- Evolution to 5G and 6G: As a foundational spectrum for 5G, CBRS will play a vital role in the transition to 6G, supporting a diverse range of applications.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The stability and reliability offered by CBRS support a broad array of IoT devices, enabling advancements in smart cities, homes, and industrial IoT applications.
- Global Spectrum Sharing Initiatives: The successful deployment of SAS could inspire other countries to adopt similar spectrum-sharing models, furthering the globalization of efficient wireless communication.
10. Conclusion: The Importance of Google SAS in CBRS Spectrum Sharing
- Innovative Spectrum Sharing Model: By enabling a collaborative approach to spectrum management, CBRS and SAS are at the forefront of modern wireless network innovation.
- Promoting Accessibility and Reliability in Wireless Communication: The architecture and components of Google SAS have paved the way for the broader adoption of wireless networks, supporting the future growth of smart and connected infrastructures.